Introduction to R
Author: Team BioSakshat
Last update: June 2017
Copyright © 2017 BioSakshat, Inc. All rights reserved.
Lets Begin
We assume that R or Rstudio is installed. R is an integrated suite of software facilities for data manipulation, calculation and graphical display.
In all the documents, the R codes written in shaded box are the codes which you can copy and try in R console. The results are shown in unshaded box.
Lets first understand the difference between expression and assignment statements in R.
Expression
Expressions are evaluated, results are printed. Results are not stored.
Semicolon ‘;’ is optional to end a statement. Its recommended to give ; at the end of each statement.
# (Hash), is used to comment single line.
# Space around + is optional but code looks clean. So recommended. Statement is not executed.
2 + 5; ## [1] 7Lets explore some more. You can use R console as calculator.
2 * 3; ## [1] 6Assignment
An assignment is a statement which is evaluated and result is stored but results of the evaluation are not printed on console.
Right hand side is evaluated whose results is stored in left hand side.
Either use = or <- as Assignment operator.
# In this example value of x will be 2.
x=2; # 2 will be assigned to x; Value of x will not be printed on console.
x <- 2+5;
x;## [1] 7Working directory
# Present working directory
getwd();## [1] "E:/BioSakshat/Gitprojects/LearnR_website"# setwd(): change the working directory by passing path of new directory.
# Enclose the path between " " (double quotes)
setwd("/home/user/")List of objects in workspace/environment
# Lists all objects/variables created in the workspace/environment
ls();## [1] "x"# rm():Delete provided object
rm(x); getting help in R
# Access to R documentation
help.start()
# Help on mean
?mean
help(solve)
# More depth search
??mean
# Explore examples on mean
example(mean);Some things to Remember
- R is case sensitive
- ; is ends a statement
- # is used to comment
Data Types
Every programming language deals with data. It is important to understand what kind of data you are dealing with and how you are going to store this. You can refer these two concepts as Data types and Data structures respectively. First we will start with data types and then move to data structures.
Data can be either in the form of integer, numeric, character or logical/boolean (TRUE/FALSE). Thus based on kind of data, data types in R can be broadly categorized into 5 categories
- Integer (int): Represents integer data such as -2, 0, 2.
- Numeric (num): Represents integers as well as decimals such as 2, 2.3, -2.3.
- Logical (logi): Represents boolean values such as TRUE and FALSE. One can also write T and F respectively. It is important to note about the case sensitivity while dealing with logical/boolean data. If you write true/false/True/False/t/f, it will not considered as logical data types (Everything has to be capital T/TRUE/F/FALSE).
- Character (chr): Represents single character (e.g. ‘M’, ‘F’) or multi-character string (e.g. ‘ABC’,‘DEF’) data. Both single (’) and double quotes (“) can be used to store character data (‘ABC’,”ABC“).
- Factor: Stores categorical data. We will explain this in detail in later sections.
Data Structures
Depending on the data, it can be stored in different way which defines the data structure. In R, data can be stored in 5 different ways, in the form of vector, matrix, array, data frames and list.
- Vector (One dimensional, Homogeneous)
- Matrix (Two dimensional, Homogeneous)
- Array (Multi dimensional, Homogeneous)
- Data frames (Two dimensional, Heterogeneous)
- List (Multi-component, Heterogeneous)
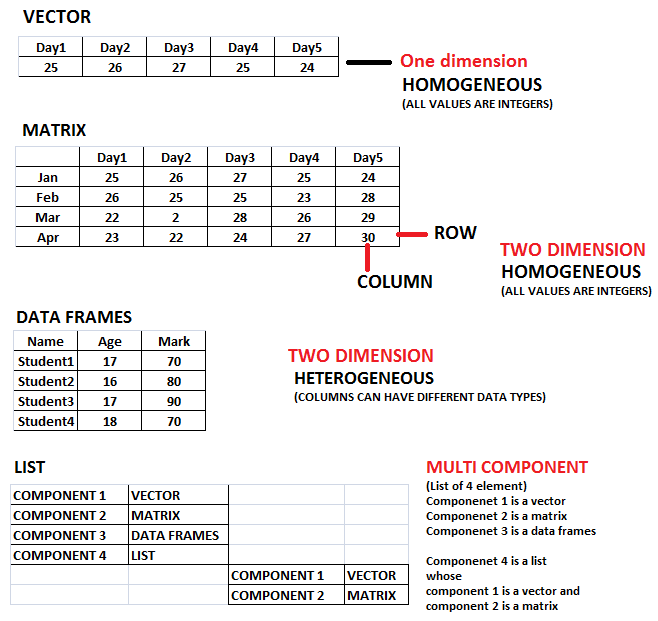
Figure 1: Data structures in R