Task
Author: Team BioSakshat
Last update: June 2017
Copyright © 2017 BioSakshat, Inc. All rights reserved.
Tasks
Vector creation
- Create a vector x13 with values 2, 3, 4, 5, 6
- Create a vector x14 with values 2.0, 2.1, 2.2, 2.3, 2.4, .., 4
- Create a vector x15 with 10 random values between 4 and 6
- Create a vector x16 with repeated values 3, 4, 5, 3, 4, 5, 3, 4, 5
- Create x17 with repeated values 7,7,7,8,8,8,9,9,9
- Create a vector x18 with 10 random values between 20 and 30
- Create a vector x19 with 10 normally distributed random values
- Create a vector x20 with values of vectors x13 and x16 followed by 3, 5,10
Fetching vector elements
- Create a vector x21 with values 33,55,66,88,99. Fetch its 3rd, 5th and 2nd values
- Fetch values of x21 from 1 to 4
- Fetch values of x21 vector excluding 2nd and 3rd elements 12 Fetch last element of x21 using length()
Vector manipulation
- Create a vector x23 with values 5, 7, 6, 8, 1, 4. Delete 1st and last element. Reset the value of second element to 12. Add value 0 at the beginning of a vector x
Vector arithmetic
- Write the arithmetic expression to calculate variance of a vector. Cross check your result using var() function. Formula: Variance= sum((x-mean(x))^2) /n-1 where n is total number of elements.
- Given x, y, z coordinates of two atoms. Atom1 (1.2, 2.3, 3.4) and Atom2 (4.5, 5.6, 6.7). Find distance between 2 atoms. Formula: sqrt((x2-x1)2+(y2-y1)2+(z2-z1)^2)
- Find out the numbers between 1 to 100, which are divisible by 2 or 3.
Matrix
- Create a matrix from a vector consisting of numbers from 1 to 12 with 3 columns
- Fetch 2nd row. Fetch 3rd column
- Fetch the value 6
- Fetch the value 8 and 12
- Fetch the value 7, 8, 11 and 12
Data Frame
- Create a data frame of gene expression data such that
First column,“Genes”, is a character vector of 6 gene names (G1, G2, …, G6).
Second column, “C1” is a numeric vector of 6 random values from 3 to 5.
Hint: Generate random numbers using function sample(). Use R help to see the syntax of sample.
Third column, “C2” is a numeric vector of 6 random values from 3 to 5.
Fourth column, “T1” is a numeric vector of 6 random values from 5 to 7.
Fifth column, “T2” is a numeric vector of 6 random values from 5 to 7.
Sixth column, “Pathway” is a character vector of which first 3 represent one pathway “P1” and other 3 represent pathway “P2”.
- Fetch values of column T2
- Fetch values of gene G2
- Fetch value of gene G3 from C2
- Delete column C2
- Insert column C3, which should be numeric vector of 6 random values from 3 to 5.
- Find mean of column C1
Tasks on Iris data set
- Open iris data set file using read.table() and store in a variable names “iris_data”
- Check the structure of “iris_data”. Note the column names. How many categories are there in column named as “Species”. Note the names of species.
- How many rows and columns are there?
- How many observations (rows) are there for each species?
- Number of rows with Species as setosa
- Number of rows with Species as virginica
- Number of rows with Species as versicolor
- Find the mean of all sepal lengths.
- Find the mean of sepal lengths in Species setosa.
- What is the overall correlation between Sepal length and Petal length?
- What is the correlation between Sepal width and Petal width of Species virginica?
- Find the difference between sepal lengths of species setosa and versicolor. What is the mean difference between them?
- Carry out the t-test between sepal lengths of species setosa and versicolor. Is it statistically significant?
Visualization
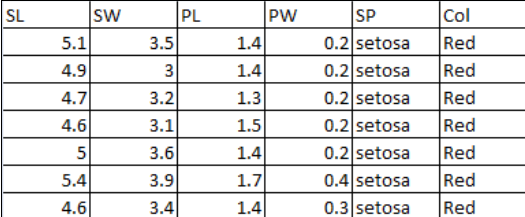
You are provided with an excel file “iris.xls”. The file contains IRIS data, 150 flowers, Categorized into 3 plants (SP:Setosa/Versicolor/Virginica) and two colors (Col:Red/Blue).
The data consists of SL (Sepal length), SW (Sepal width), PL (Petal length) and PW (Petal width) in cm.
Task: Load the data in R using appropriate function and extract useful information by data visualization.
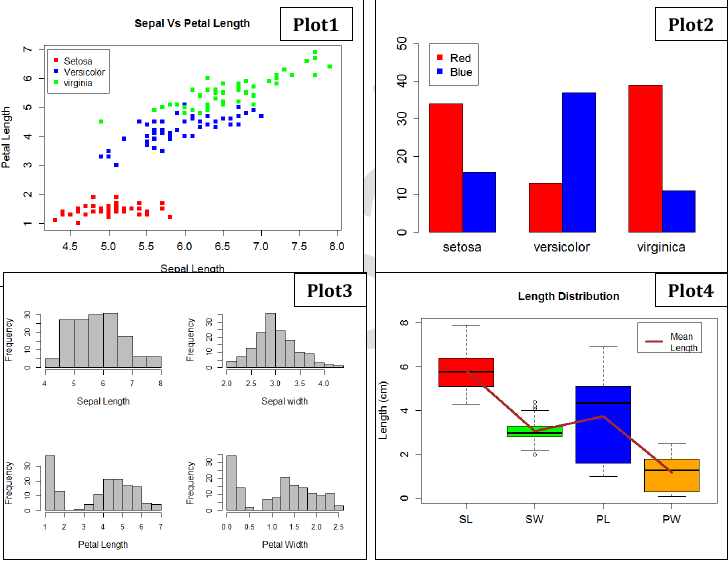
- Plot1: Scatter plot of Sepal length vs Petal length of all 150 flowers, color according to species/plants.
- Plot2: Barplot showing distribution of Sepal lengths among 6 classes of flowers (3 plants and 2 colors).
- Plot3: Multi panel plot showing the histogram of SL, PL, SW, PW of all 150 flowers.
- Plot4: Box plot showing SL, SW, PL, PW distribution along with a line joining their mean lengths.
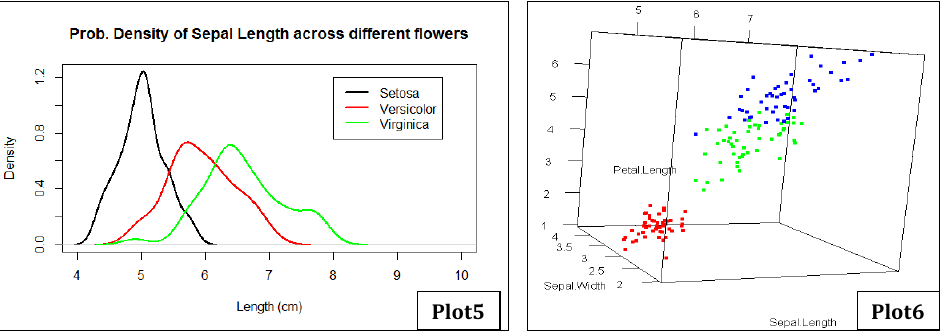
- Plot5: Probability density plot of Sepal lengths among three different categories of plants.
- Plot6: 3D plot showing distinct clustering of flowers in terms of SL, SW and PL. Different colors for different plants.
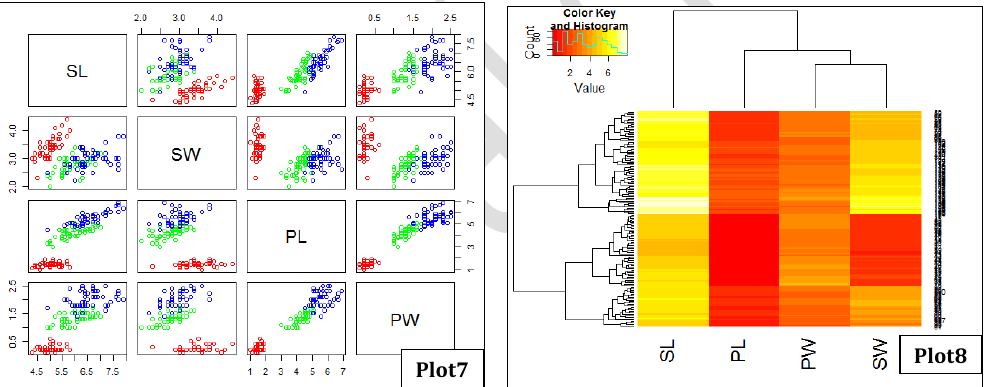
- Plot7: Scatter plot matrix showing a global view of the distribution of SL, SW, PL and PW across 3 plants.
- Plot8: Heatmap showing clustering of flowers in terms of their SL, SW, PL and PW properties.
- Plot9: Pie chart showing the number of flowers in 6 categories (3 plants and 2 colors)
- Plot10: Dot chart showing clear distribution of SL among 3 plants.